VCP-VCF Administrator Exam Community Study…
This is session #2 of our Study Group. Covered areas are listed below:
This is session #2 of our Study Group. Covered areas are listed below:
If you have been following my recent adventures in playing with both Authentik and Keycloak as an OAuth/OIDC Identity Provider (IdP) for use with vCenter Server or VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) Identity Federation, you can take it one step further and authenticate with a Yubico YubiKey or Apple […]
Join our #vmwarecode community-led study groups for support! These groups are meeting weekly at 9 AM EST to break down core concepts from the official exam guide. It’s a collaborative, open space—no rigid lessons, just community-driven discussions, resources, and insights.
When troubleshooting ESXi network and Syslog server connectivity issues, knowing the right tools can save you hours of frustration. Whether it’s an unresponsive syslog server, blocked TCP/UDP ports, this guide will help you diagnose and fix common connectivity issues quickly.
Key Troubleshooting Tools for ESXi Network Connectivity
Before checking anything else, confirm that the ESXi host can communicate with the syslog server at a basic network level.
Standard ICMP ping test:
ping <destination-IP>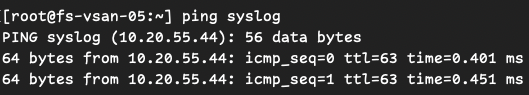
VMkernel-specific ping (useful for vMotion, NFS, etc.):
vmkping <destination-IP>or specify which vmkernel should be used as ongoing interface for ping
vmkping -I vmk0 <destination-IP>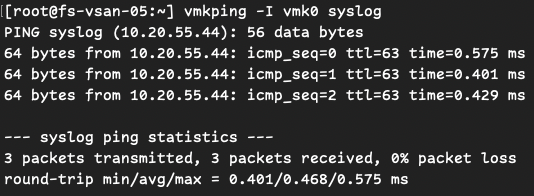
If these fail, the issue is likely a network routing problem or an upstream firewall blocking traffic.
Even if the server is reachable, the syslog port might be blocked or not listening. Netcat helps determine if a specific TCP or UDP port is reachable.
⚠️ Note: Be aware that netcat doesn’t display an error message when a connection fails—only a successful connection is reported.
Use Cases
Test TCP Port Connectivity:
nc -z <destination-ip> <destination-port>Test UDP Port Connectivity:
nc -zu <destination-ip> <destination-port>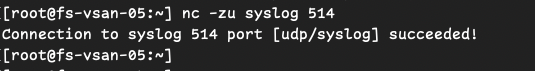
ESXi provides tools to inspect active network connections and adapter performance.
Check active TCP/UDP connections:
esxcli network ip connection list|grep <port>
If the syslog connection isn’t listed, ESXi isn’t attempting to send logs—double-check your syslog configuration in vSphere.
Check NIC statistics for errors and dropped packets:
esxcli network nic stats get -n <vmnicX>
Persistent errors here could indicate network congestion or misconfigurations.
Troubleshooting network issues between an ESXi host and a syslog server doesn’t have to be a headache. Using these tools, you can pinpoint the problem—whether it’s a blocked port, misconfiguration, or network adapter issue—and resolve it efficiently.
Still facing issues? Look at Broadcom KB
The introduction of VPCs (Virtual Private Cloud) at the network level provides a “self-service” for network, security and other network services in an isolated environment. Those responsible for the VPC can create networks and security rules (within their limits), thus relieving the burden […]
As I’ve received some questions on this topic, I figured I would write a quick article that describes the concept of site maintenance. Note that in a future version of vSAN, we will have an option in the UI that helps with this, as described here. […]
As enterprises continue to embrace hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, VMware’s partnerships with leading cloud providers have opened the door for seamless workload migrations and modernized IT […]
In VMware ESXi, managing physical network interfaces (vmnics) is essential for troubleshooting, maintenance, or reconfiguration. There are times when you need to disable or re-enable a network interface without relying on the network team to shut down a switch port or physically unplugging the cable in the server room. Fortunately, this can be done quickly using the esxcli command-line tool.
First login via SSH or directly on server console.
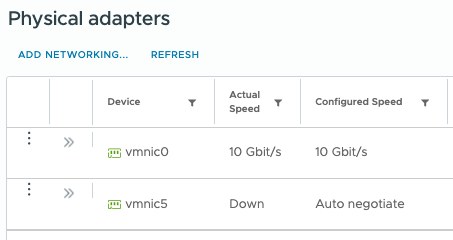
Before shutting down a vmnic, it’s good practice to list all available interfaces and check their status:
esxcli network nic list
This command will display a list of vmnics along with their link state, driver, and speed.
To disable a specific vmnic, use the following command:
esxcli network nic down -n vmnicX
Replace vmnicX with the actual interface name (e.g., vmnic5).
If you need to enable the interface again, run:
esxcli network nic up -n vmnicXThis will bring the network interface back online.

By using esxcli, you can manage network interfaces efficiently.
Let me know if you need any tweaks! 🚀
A look at the top Docker containers for DevOps in 2025. Streamline your code projects and automation with these cool and robust containers